6.1 UNSUPERVISED NON-INVASIVE MEASUREMENT OF AORTIC PULSE TRANSIT TIME BY MEANS OF ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.225How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Objectives: This study provides first experimental evidence on the feasibility of measuring Pulse Transit Time (PTT) values within the aorta by means of non-invasive and non-obtrusive Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) technology.
Methods: A wide range of pulse wave velocity scenarios were obtained by administrating noradrenalin and nitroglycerine to an anesthetized pig under mechanical ventilation. Two arterial lines were inserted into the ascending and the descending aorta for measuring reference PTT values. EIT images were generated from 32 impedance electrodes placed around the chest at the level of the axilla. Regions of Interest (ROI) such as the descending aorta were automatically identified by a novel time-based processing algorithm as the respective EIT pixels representing these structures [1]. Aortic EIT-PTT values were determined as the delay between the opening of the aortic valve (obtained from arterial line) and the arrival of pressure pulses at the aortic ROI within the EIT plane.
Results: For 9 experimental conditions, with mean BP ranging from 73 to 141 mmHg, strongly significant correlation (r = 0.98, p<0.00001) between aortic EIT-PTT and arterial line PTT was observed (Figure 1).
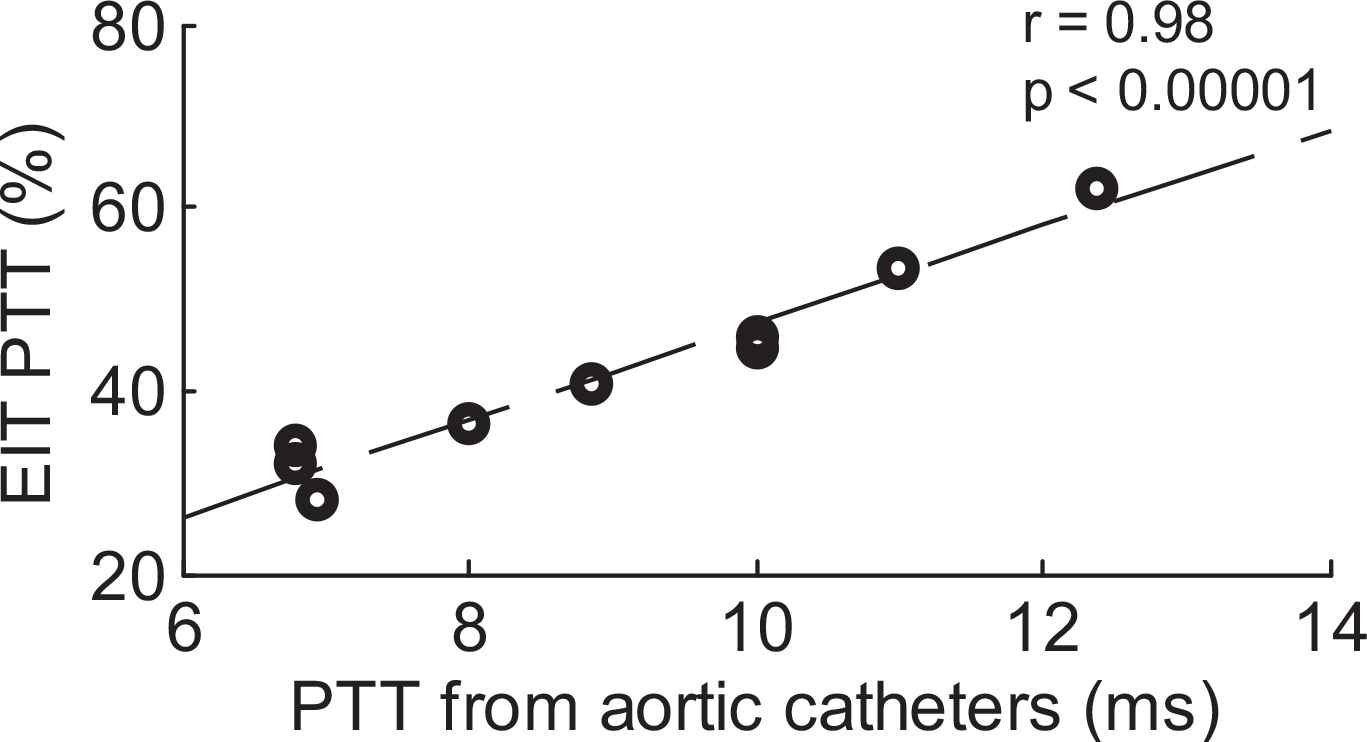
Correlation between aortic PTT as measured by arterial lines and EIT technology at different hemodynamic conditions
Conclusion: EIT is a novel candidate technology for the unsupervised monitoring of arterial stiffness.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - J. Solà AU - A. Adler AU - A. Santos AU - G. Tusman AU - F. Suárez Sipmann AU - S.H. Bohm PY - 2011 DA - 2011/11/29 TI - 6.1 UNSUPERVISED NON-INVASIVE MEASUREMENT OF AORTIC PULSE TRANSIT TIME BY MEANS OF ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY JO - Artery Research SP - 144 EP - 144 VL - 5 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.225 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.225 ID - Solà2011 ER -
