P2.10 MECHANISTIC INSIGHTS INTO THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN WAVE REFLECTION AND RETINAL ARTERY FLOW PULSATILITY
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.031How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
Background:Increased arterial stiffness is associated with a reduced buffering capacity of the large arteries, therefore predisposing the microcirculation to increased flow and pressure pulsatility. Previous data from our group have illustrated a positive relationship between aortic pulse wave velocity and an inverse relationship between wave reflection and retinal artery flow pulsatility.Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the macrovascular haemodynamic mechanisms involved in retinal artery flow pulsatility, by manipulation of wave reflection by Glycerol Trinitrate Nitrate administration.
Methods: Nine individuals, aged 63±6 years and free from CV acting medication participated in this study. Augmentation index (AIx) was recorded using the SphygmoCor system (Atcor) as a measure of wave reflection. Pulsatility index (PI), a measure of retinal artery flow pulsatility was recorded using doppler ultrasound (GE) and both peripheral and central blood pressure were measured using the Mobilograph system (IEM). All vascular haemodynamic measurements were recored simultaneously at basline and then again at 1,3,5,10 and 15 minutes post GTN administration.
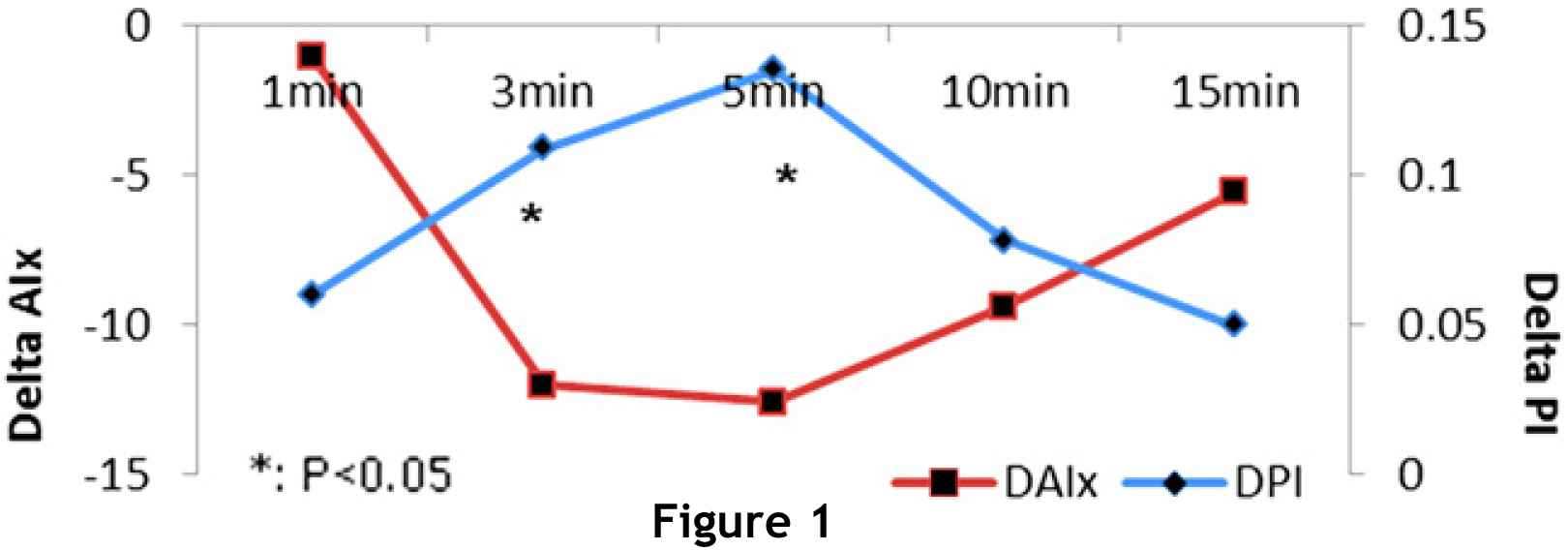
Results: The relationship between AIx and PI change from baseline were significantly different at 3 and 5 minutes (P=0.02 and P=0.03, respectively). See figure 1.
Conclusion: This study illustrates a direct inverse relationship between AIx and retinal artery flow pulsatility, suggesting a direct link between large artery haemodynamics and pulsatile flow in the microvasculature.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - B.J. McDonnell AU - J. Coulson AU - M. Zagura AU - M. Munnery AU - E. Stohr AU - R. Shave AU - C.M. McEniery AU - I.B. Wilkinson AU - J.R. Cockcroft PY - 2011 DA - 2011/11/29 TI - P2.10 MECHANISTIC INSIGHTS INTO THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN WAVE REFLECTION AND RETINAL ARTERY FLOW PULSATILITY JO - Artery Research SP - 155 EP - 155 VL - 5 IS - 4 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.031 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2011.10.031 ID - McDonnell2011 ER -
