P.101PULSATILE ARTERIAL PRESSURE IS PREDOMINANTLY DETERMINED BY THE CENTRAL RESERVOIR, WHICH CAN BE DETERMINED NON-INVASIVELY FROM PERIPHERAL MEASUREMENT SITES
- DOI
- 10.1016/j.artres.2007.07.035How to use a DOI?
- Open Access
- This is an open access article distributed under the CC BY-NC license.
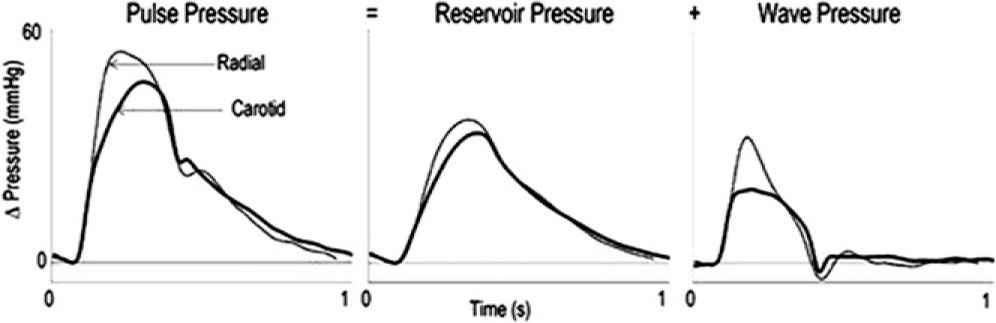
Introduction: There is a large variation in the pulse pressure waveform in systole throughout the arterial system. However, at these corresponding sites, the diastolic phase appears almost identical. We hypothesise that this is because diastolic pressure is predominately determined by the reservoir properties of the central elastic arteries, despite large differences in wave reflection and local compliance of peripheral arteries themselves. We assessed the contribution of the central reservoir to the peripheral pulse pressure waveform.
Method and Results: Pressure and flow velocity were measured non-invasively at right common carotid and radial arteries in 14 healthy volunteers (49±11 years) using tonometry, calibrated to brachial blood pressure, and Doppler ultrasound. We calculated the reservoir pressure and compliance (local pulse wave velocity). The time constant of diastolic decay (τ) was calculated from the exponential rate of decline in pressure during diastole. Reservoir pressure was the largest overall contributor to pulse pressure in the carotid (28.0±4.8mmHg; 53±6%), and radial (32.0±6.2mmHg; 48±4%). τ was similar in each artery (carotid: 427±281ms versus radial: 427±320ms (p>0.99) despite large differences in local pulse wave velocity (carotid: 7.2±2.6ms−1 versus radial: 10.9±5.0ms−1, p<0.05).
Conclusion: The reservoir is the largest determinant of pulse pressure and is similar in central and peripheral arterial sites, despite significant variation in local compliance. Estimation of reservoir pressure in the radial artery may be a simple and useful indicator of the properties of the aorta and large elastic arteries.
Cite this article
TY - JOUR AU - J.E. Davies AU - A. Malaweera AU - N. Hadjiloizou AU - K.H. Parker AU - J. Aguado-Sierra AU - J. Mayet AU - D.P. Francis AU - A.D. Hughes PY - 2007 DA - 2007/08/30 TI - P.101PULSATILE ARTERIAL PRESSURE IS PREDOMINANTLY DETERMINED BY THE CENTRAL RESERVOIR, WHICH CAN BE DETERMINED NON-INVASIVELY FROM PERIPHERAL MEASUREMENT SITES JO - Artery Research SP - 76 EP - 76 VL - 1 IS - 2 SN - 1876-4401 UR - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2007.07.035 DO - 10.1016/j.artres.2007.07.035 ID - Davies2007 ER -
